Hydrogen
Hydrogen production is a critical topic in the current industrial landscape due to its use as a raw material in the chemical industry, as well as its key role in the energy transition.
Hydrogen is gaining increasing interest in energy transition projects and is expected to play a significant role in the energy mix. Although it is currently used primarily in the chemical and refining industries, it also serves as an energy carrier, offering a compelling alternative to fossil fuels. It is an inexhaustible and non-polluting fuel that enables the storage of energy produced by major renewable energy sources.
Since hydrogen is almost nonexistent in its molecular form in nature, it is mainly obtained through the following production methods:
- Reforming or gasification of hydrocarbons.
- Thermochemical dissociation of water or biomass.
- Water electrolysis.
Process simulation plays a crucial role in hydrogen production by optimizing design, reducing costs, and speeding up the development of innovative technologies. With our comprehensive range of simulation software and expertise, you can anticipate performance, minimize risks, and maximize the efficiency of your hydrogen projects.
Raw material processing
As with most processes in the chemical industry, hydrogen production requires an initial step dedicated to raw material processing.
The ProSimPlus software offers the necessary features and modules to conduct studies related to raw material processing (membrane filtration, distillation columns, absorption columns, separation vessels, etc.). In this context, ProSim DAC software can also be used for dynamic simulation of adsorption columns.
Application cases:
- Water purification upstream of an electrolyzer
- Natural gas treatment (more information in the gas industry section)
- Air separation unit
- Adsorption on activated carbon
- And more…
Application examples:
- Seawater desalination using different technologies: distillation or membrane filtration: PSPS_EX_EN-Seawater-Desalination
- Natural gas dehydration with TEG: PSPS_EX_EN-Gas-Dehydration-TEG
- Natural gas sweetening using the Selexol process: PSPS_EX_EN-Selexol-Process
- Additional examples available upon request…
Hydrogen production
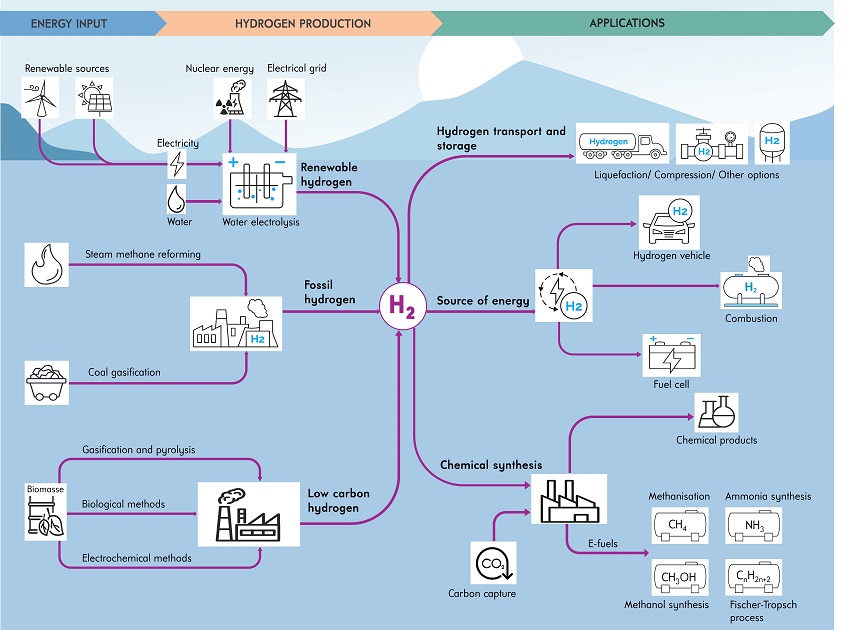
There are different methods of hydrogen production, which can be classified based on the type of hydrogen produced.
Renewable Hydrogen
To produce decarbonized hydrogen, a renewable energy source (solar, wind, hydroelectric, nuclear, etc.) is used to generate the electricity needed to power the electrolyzer.
The ProSimPlus software includes an electrolyzer module, which allows for the representation of the three main electrolyzer technologies: alkaline, PEM (Proton Exchange Membrane), and SOEC (Solid Oxide Electrolysis Cell).
Fossil Hydrogen
Fossil hydrogen production is primarily achieved through steam reforming of natural gas and coal gasification. The various unit operations involved in these processes are available in the ProSimPlus software (boiler, reactor, two-phase separator, etc.).
Low-Carbon Hydrogen
Hydrogen production from biomass utilizes organic materials. This approach allows for the valorization of agricultural and forestry waste, contributing to the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions. There are three main pathways for producing hydrogen from biomass: biological treatment, electrochemical conversion, or thermochemical methods (primarily through biomass gasification and pyrolysis).
The ProSimPlus software, and potentially the BatchReactor and BatchColumn software, are particularly well-suited for addressing the challenges related to modeling processes that use bio-based raw materials.
More information can be found in the bio-based industry section.
Application examples:
- Hydrogen production from alkaline electrolysis: PSPS_EX_EN-Hydrogen-Production-Electrolysis
- Simulation of an integrated gasification combined cycle: PSPS_EX_EN-IGCC-Power-Plant
- Hydrogen production from hydrocarbon reforming: PSPS_EX_EN-Three-Combined-Cycle-Power-Plant; PSPH_EX_EN-Ammonia-Synthesis-Process
- Additional examples available upon request…
Hydrogen applications
This section presents the various applications of hydrogen and thus addresses the processes that occur downstream of hydrogen production: hydrogen storage and transport, its use as an energy source, and the different chemical synthesis pathways.
Storage & transport
Hydrogen storage is primarily conducted in tanks, either in gaseous form through compression or in liquid form through liquefaction. Hydrogen can also be adsorbed (physisorbed) or absorbed (chemisorbed) by materials (hydrides) that are in solid form.
The ProSimPlus software can be used to model hydrogen liquefaction or compression processes, as well as to calculate pressure drops in pipelines. The ProSec software is also particularly relevant in this field and can be used to simulate brazed plate multi-fluid heat exchangers. ProSim DEP is useful when users want to perform dynamic simulations of hydrogen storage tank filling and emptying or conduct risk assessments related to storage.
Application examples:
- Hydrogen liquefaction: PSPS_EX_EN-PRICO-Process-Natural-Gas-Liquefaction
- Rigorous modeling of a brazed plate heat exchanger using ProSec: COPROSEC_EX_EN-Ortho-Para-Hydrogen-Conversion
- Additional examples available upon request…
Energy sources
Hydrogen is an energy carrier. Once produced, it can be directly consumed to generate electricity or thermal energy.
The ProSimPlus software includes specific modules (such as the “fuel cell” module and the “boiler” module) that facilitate the simulation of this part of the process.
Application examples:
- Combined cycle power plant: PSPS_EX_EN-Combined-Cycle-Power-Plant
- Additional examples available upon request…
Chemical synthesis
Hydrogen is a raw material frequently used in the chemical industry. It is particularly essential for the production of e-fuels, which are among the promising solutions to address current energy challenges. Several synthesis pathways are currently employed, leading to various types of e-fuels: Fischer-Tropsch process, methanol synthesis, methanation, ammonia synthesis, and more.
The ProSimPlus software is a leading reference for modeling these types of processes.
Application examples:
- Toluene Hydroalkylation process using hydrogen and benzene: PSPS_EX_EN-Cost-Analysis-HDA-Toluene
- Cyclohexane synthesis: PSPS_EX_EN-Cyclohexane-Production-Unit
- Methanol synthesis: PSPS_EX_EN-Methanol-Synthesis
- Ammonia synthesis: PSPS_EX_EN-Ammonia-Synthesis-Process
- Additional examples available upon request…
CO2 capture
The topic of hydrogen is often linked to CO2 capture and utilization issues. To reduce greenhouse gas emissions, it is crucial to capture CO2 and, when possible, convert it into valuable products.
CO2 capture is commonly performed using absorption columns. Modeling these unit operations requires representing the complex physical phenomena involved. Leveraging its expertise in thermodynamics, the technical team at Fives ProSim is highly active in this area and routinely assists users to ensure rigorous modeling of their technologies.
Application examples:
- CO2 capture from the amine production process: PSPS_EX_EN-CO2-Capture-Amine-Process
- CO2 capture using the Rectisol process: PSPS_EX_EN-Rectisol-Process
- CO2 capture using the Purisol process: PSPS_EX_EN-Purisol-Process
- CO2 capture using the Selexol process: PSPS_EX_EN-Selexol-Process
- Additional examples available upon request…