BatchColumn
Simulation of batch distillation columns
Users of batch distillation columns (pharmaceuticals, specialty chemicals, essential oils, alcohols …) know the advantages of this process: great flexibility, a single column can separate complex mixtures, product identification, etc. They are also aware of the complex phenomena at play, where there is no ‘rule of thumb’ to achieve the optimal solution: reduced operating time, good product separation, minimum energy consumption, etc. BatchColumn was developed specifically to overcome these challenges.
Main features
Rigorous dynamic model that is fully configurable (semi-batch, multi-fraction operation …)
Detailed representation of the heating system, hydrodynamics of the column, condenser / decanter and associated controls
Optimization of the most complex separations (azeotropic, extractive, reactive …)
Reliable description of the production recipe (filling, total reflux, variable reflux …)
User-friendly interface, fast calculation and easily exploitable results
Dedicated to the simulation of the behavior of a batch distillation process. 
Its flexibility and robustness for the most complex separations and its user friendliness makes it a unique tool used and prized by the largest chemicals and international engineering companies.
BatchColumn is a comprehensive simulation tool for design, analysis and optimization of batch distillation processes. The software comes with an easy-to-use graphical user interface, rigorous thermodynamics and model library for batch distillation, run-time interaction, custom modeling capabilities and rigorous numerical solvers.
BENEFITS:
- Easy simulation environment to learn and use
- Improve productivity
- Flexibility to model the reality
- Improved yields
- Increased capacity
- Reduced batch cycle times
- …
Hardware requirements
Intel (or equivalent) based PC with:
- Computer running Windows (7, 8, 8.1, 10, 11) or Windows Server (2012R2, 2016, 2019, 2022)
- x86 or x64 processor running at 1 Ghz minimum (or 2 vCPUs for a virtual machine)
- RAM: 4 GB minimum (plus 2 GB per concurrent user for a server)
- Storage: 4 GB minimum (plus user file storage)
- Internet access: only to download the software and the license.
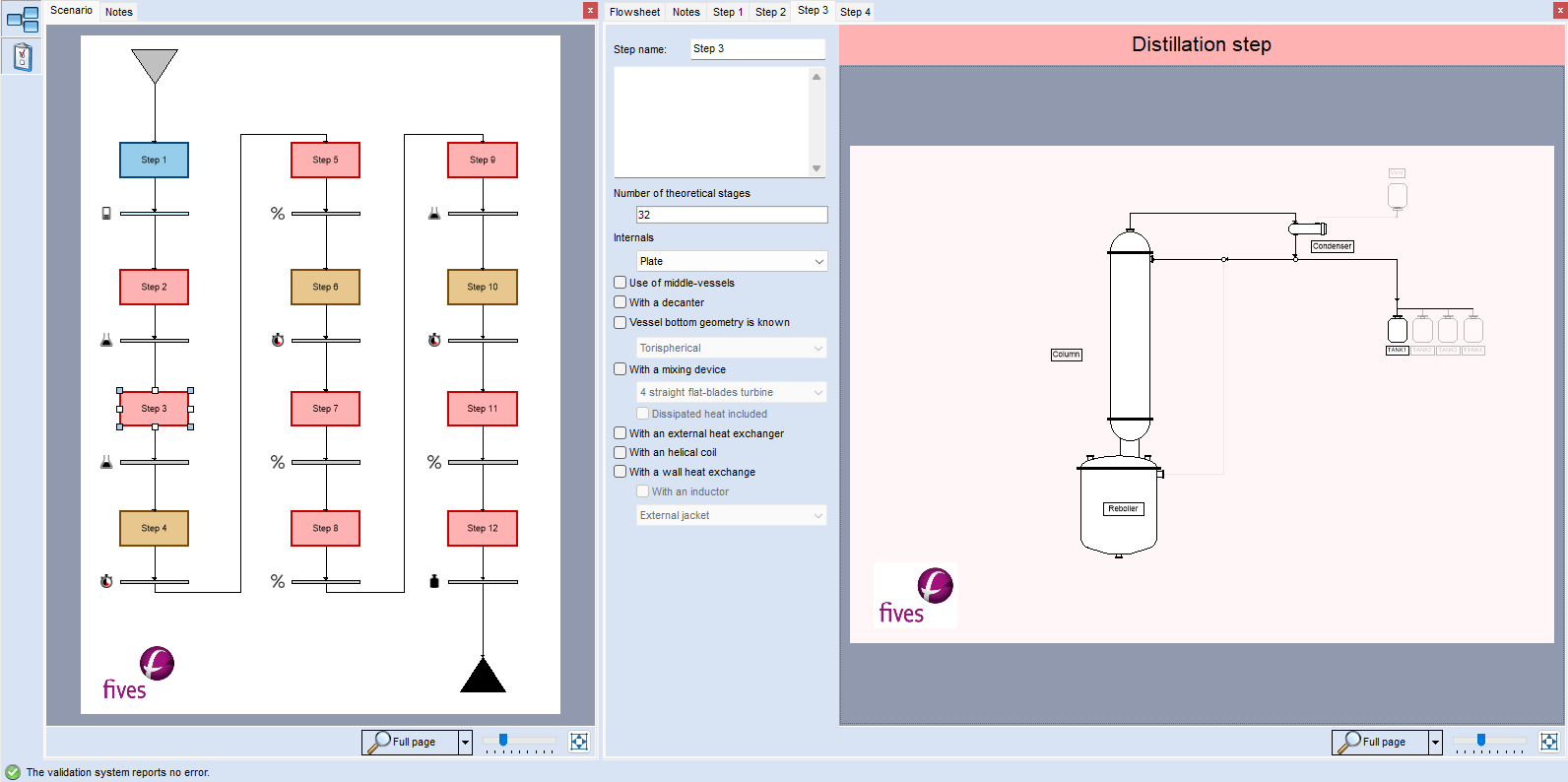
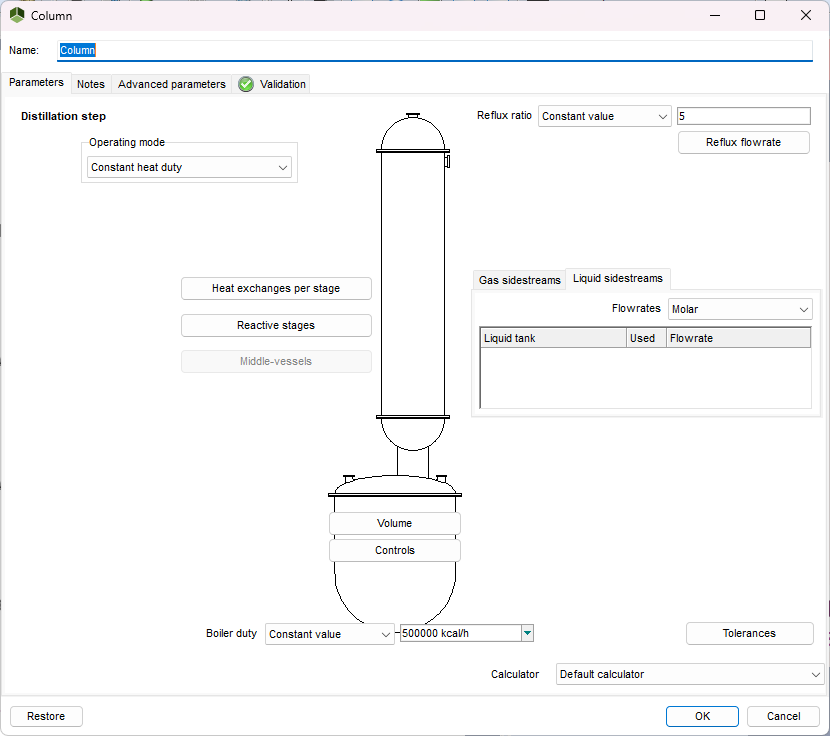
A very detailed representation of the column and associated equipment
Equipment specification: column, boiler, condensers… each piece of equipment is defined with the appropriate level of detail to meet your objectives.
The equipment can be chosen from a standard library or customized for the following:
- vessel bottom: flat, hemispherical…
- wall heat exchangers (half-shells, double envelop) with external circulation or immersed (coils)
- mixing devices: turbine, impeller…
- wall materials: vitrified steel…
- thermal fluids
A software tool (Simulis Technologies) allows you to create and manage a list of the equipment used specifically by your company.
One of the best thermodynamics packages available on the market!
In distillation, the quality of the simulation depends, above all, on correct values for vapor-liquid equilibria (or liquid-liquid-vapor) and other physico-chemical properties of the fluids in the column. BatchColumn models complex systems by taking advantage of the power of Simulis Thermodynamics:
- an extensive set of thermodynamic models selected for their reliability and robustness (SRK, NRTL, UNIFAC …)
- a property database of more than 2,300 pure components (AIChE’s DIPPR database)
- mixture property and phase equilibrium calculations for many different thermodynamic models
- Property estimation, able to use in-house proprietary databases, etc.
Instantaneous, equilibrium, reversible, and irreversible chemical reactions that can also take into account the kinetics (Arrhenius, Langmuir Hinshelwood…) allows BatchColumn to efficiently simulate reactive distillations.
Learn more about to Simulis Thermodynamics
Test alternative synthesis routes and new production strategies
The distillation recipe is described as it would be in an industrial unit… by a series of operating steps. At each step, a different operating mode can be defined:
- start-up from a steady-state or filling of the column to reach a state of pre-defined trays
- distillation with fixed or variable reflux (for example, to achieve a desired distillate component purity)
- distillation with an infinite reflux or a fixed reflux (where the distillate is returned to the boiler)
At each step, it is possible to modify any of the operating parameters:
- reflux policy: ratio, reflux phase
- collection tank for the distillate
- operating pressure (constant, as a function of time…)
- flow rate and temperature of the cooling fluid at the level of each condensing stage
- feeds and product collection (open, closed, flow rates)
- temperature, hot fluid flow rate for the boiler, parameters of the mixing system
- stopping or starting the use of a decanter
- which chemical reactions to use…
Steps are sequenced automatically through the detection of events described by the user. These events can be based on operation duration, an amount of product, tray temperature, product purity in a collection tank, achieved reflux ratio…
Easy-to-use interface, fast calculations and easily exploitable results
The intuitive graphical user interface makes it easy to enter the required information for any batch distillation, even the most complicated configurations.
With its robust and efficient numerical methods, BatchColumn easily handles complex cases: highly non-ideal mixtures, processes with discontinuities.
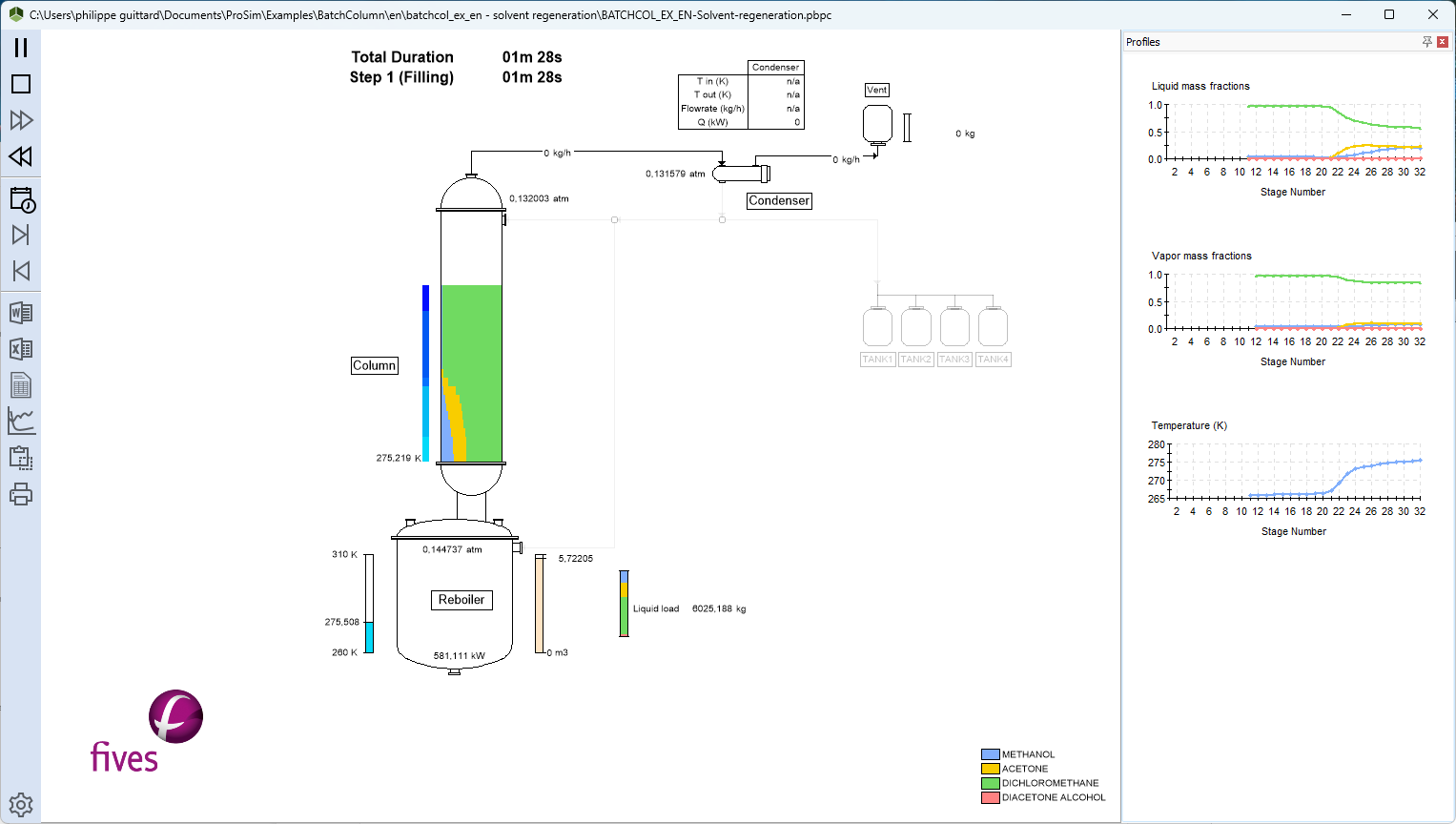
During the simulation, BatchColumn graphically and numerically displays the evolution of basic parameters (composition profiles in the column, temperature, pressure, reflux ratio…). At the end of the simulation, results are available in graphical format (with respect to time), tables, and exportable text.
- Batch distillation flowsheet – simulator
- thermodynamic calculation, study, analysis
- distillation column configuration
- graphical simulation – Simulation of batch distillation columns
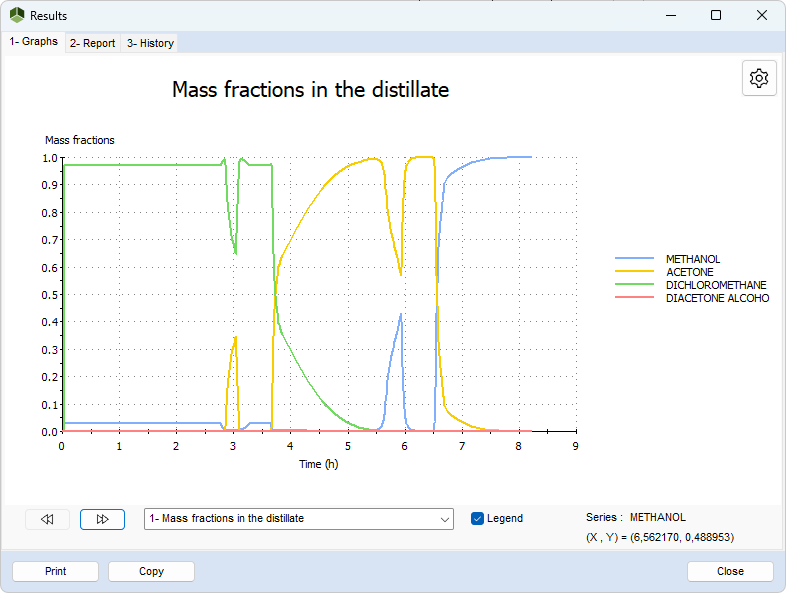
- Mass fraction in the distillate
BatchColumn demonstrates to be very useful to:
- optimize the required heating power , reflux ratio, and time required for each fraction or cut,
evaluate the VOC emissions, - reduce batch times and product waste,
- quickly design procedures for separating new mixtures,
- develop a control strategy for safety reasons,
- minimize energy consumption,
- study warm-up and shutdown procedures ,
- reduce the number of preliminary pilot plant tests,
- store the knowledge learned during a separation simply by archiving its model…
Application examples
- Optimization for the separation of the mixture: Isopropanol/Water/Ethanol/1-4 Dioxan/Ethylacetate/ Dimethylacetamide
- Water/Acetonitrile/ Toluene/Methanol
- Simulation and optimization of a distillation column with Acetone/Water/IPA
- Simulation and optimization of a distillation column with Water/Sodium hydroxide/Sodium chloride/IPA/Methanol
- Isopropanol regeneration
- Batch distillation of very pure Ethanol
- Design of a trichloroanisole distillation column
- Study of a reconcentration column